Application of RFID Technology in Coal Mine Safety Production
1 Overview RF ID technology is a new automatic identification technology that directly inherits the principle of radar and develops it. The use of reflected power for communication lays the theoretical foundation for RFID. The problem of RFID standardization is increasingly valued by people. The variety of RFID products is more abundant, and the scale application industry is expanding. Especially the use of Wal-Mart and the US military has greatly promoted the research and application of RFID. In South Africa, RFID technology has been successfully used in mine management, successfully solving problems in mine management such as mine attendance, anti-theft, and safety. The degree of integration of domestic mining area management and computer is mainly limited to the uphole part, including daily business process management, accounting management, and transportation management. Coal mine management still takes experience management as the core. With the development of informationization and networking in the coal industry, most coal mine enterprises have adopted various coal mine management systems in the actual production process, and in practical applications. Played an important role. With the introduction of RF ID technology, domestic coal mines have begun to use RFID technology for management. Such as: Xishan Mining Bureau, Datong Mining Bureau. 2 basic composition and working principle RF ID technology is a non-contact automatic identification technology. Its basic principle is to use the RF signal and spatial coupling transmission characteristics to realize automatic recognition of the identified object. The system generally consists of three parts, namely an electronic tag, a reader, and an application interface. The space coupling between the electronic tag and the reader is realized by the coupling element, and in the coupling channel, energy transfer and data exchange are realized according to the timing relationship. The basic model of the system is shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that in the working process of the RF ID system, data is always exchanged through a certain time series on the basis of energy. The reader provides working energy to the electronic tag. When the electronic tag enters the RFID field, the RF wave emitted by the reader activates the tag circuit, interacts, and completes the exchange of data. For multi-tag simultaneous reading, you can use the form of the reader first, or the form of the label first. In order to realize multi-tag conflict-free simultaneous reading, the reader first issues an isolation command to a batch of tags, so that multiple electronic tags in the reading range of the reader are isolated, and finally only one tag remains in the reader. The active state establishes a conflict-free communication link with the reader. After the communication ends, the tag is instructed to enter sleep, and a new tag is designated to execute the conflict-free communication command. Repeat this way to complete multi-label simultaneous reading. For the label first-issue method, the label randomly sends its own identification ID repeatedly. Different labels can be correctly read by the reader in different time periods, and the multi-tag is read at the same time. For any electronic tag, it has a unique ID number, which is unchangeable for a tag. In most applications, the data attributes of the tag are supported by the use of a back-end database. Identification systems, which typically consist of electronic tags and readers, serve the application, and the needs of the application vary and vary. The interface between the reader and the application system is represented by standard functions called by the development tool. The function roughly includes the following aspects. The application system issues configuration commands and other instructions to the reader as needed. The reader returns its current configuration state and execution results of various instructions to the application system. 3 application in underground personnel positioning management To realize the effective identification, monitoring and monitoring of the entry and exit of coal mine underground workers, the management system fully reflects the "humanization, informationization and high automation" to achieve the goal of digital mines. The basic functions realized in the underground coal mine personnel positioning management include: 1 how many people are in the well or at a certain place at any time, who are these people; 2 the trajectory of each person at any time in the well; 3 query one or more The actual position of the personnel (the positioning of the underground personnel) makes it convenient for the dispatching center to quickly and correctly contact the personnel of the Australian occupation of the time and total working hours of the relevant personnel at any place, etc., and can supervise and implement important inspections. Personnel (such as gas testers, temperature testers, wind surveyors, etc.) conduct testing and processing of various data on time and at the point to fundamentally eliminate related accidents caused by human factors. The solution is to install several readers in each lane of the underground and the passage that the personnel may pass. The specific quantity and location are determined according to the actual conditions of the roadway and the functional requirements to be realized, and they are passed through the communication line and the computer of the ground monitoring center. Data exchange. At the same time, an electronic tag is placed on the miner's lamp or other equipment worn by each person who is going down. When the person entering the well goes down, the reader will sense the signal and upload it to the camera as soon as it passes or approaches any reader placed in the roadway. On the computer of the monitoring center, the computer can determine the specific information (such as: who, where, the specific time), and display it on the large screen or computer display of the monitoring center and back up, the administrator can also The distribution diagram on the big screen or on the computer clicks on a certain position in the underground, and the computer will count and display the personnel situation in this area. At the same time, the computer of the control center will sort out the various attendance reports of each person in the downtime according to the personnel's access information for a period of time (such as: attendance rate, total attendance time, late arrival and withdrawal record, no attendance time, etc.). In addition, once an accident occurs in the underground, the personnel of the accident location can be immediately detected according to the location information of the personnel in the computer, and then the detector can be used to further determine the exact position of the personnel in the accident area, so as to help the rescue personnel to rescue the vehicle in an accurate and rapid manner. Trapped people. The schematic diagram of underground personnel positioning monitoring is shown in Figure 2. 4 Application in roadway safety, statistical attendance and equipment management Different levels of people can enter different lanes. The person to be passed is automatically identified by a reader installed at the exit of the roadway. According to the information set by the background database, the revolving door at the roadway is controlled accordingly. When the person is allowed to enter, the door is automatically opened. When the person is not allowed to enter, the revolving door is closed. At the same time, the personnel who come to the entrance of the roadway are automatically recorded and saved, which is convenient for querying and generating reports. In the aspect of attendance, the exact downtime and the uptime of each person in the well are shown. According to the type of work (specified for the time of the class), it is judged whether the different types of personnel are in the class, so as to determine whether the downhole is valid. In the monthly statistical report, the classification and statistics of the downtime and the number of downholes (effective times) are easy to assess. Print monthly attendance reports, statistics on downhole statistics at any time, and other related reports. The specific real-time location of the car and other important equipment, the number of times each car is transported per day and the frequency of access, easy to manage. The setting and application principle of the device are basically the same as the positioning of the personnel. 5 Conclusion RFID is based on underground safety supervision in mine applications and can be classified according to personnel safety management, roadway safety management and safety materials management. Using RFID technology, establish information collection and processing solutions, realize information transmission and information sharing, provide support for enterprise management, and realize informatization, standardization and visualization of underground management. Maximize the safety of personnel. Flange-Mounted Pressure Filter
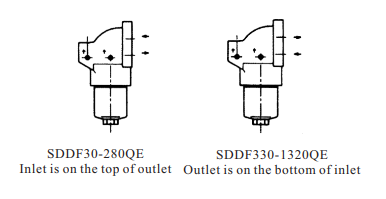
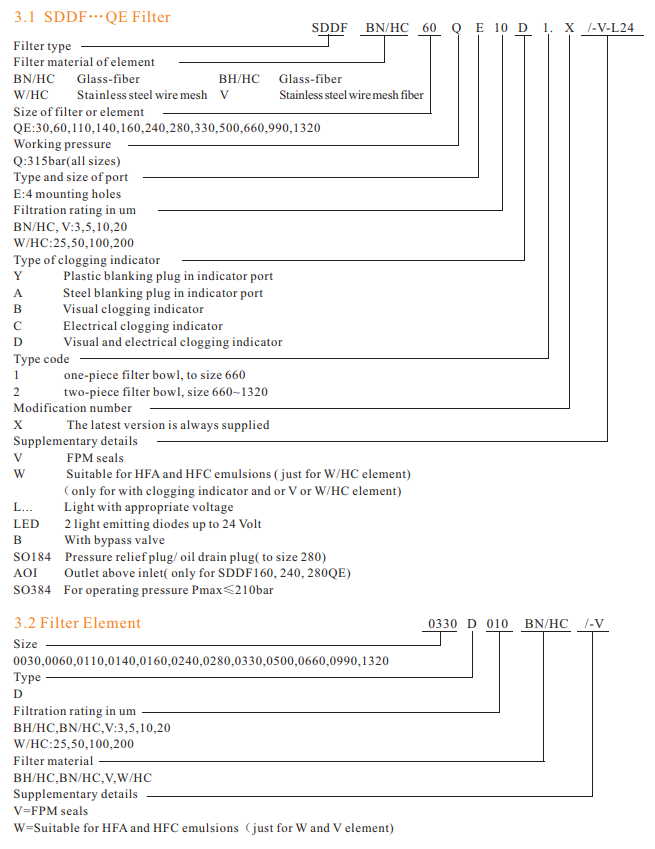
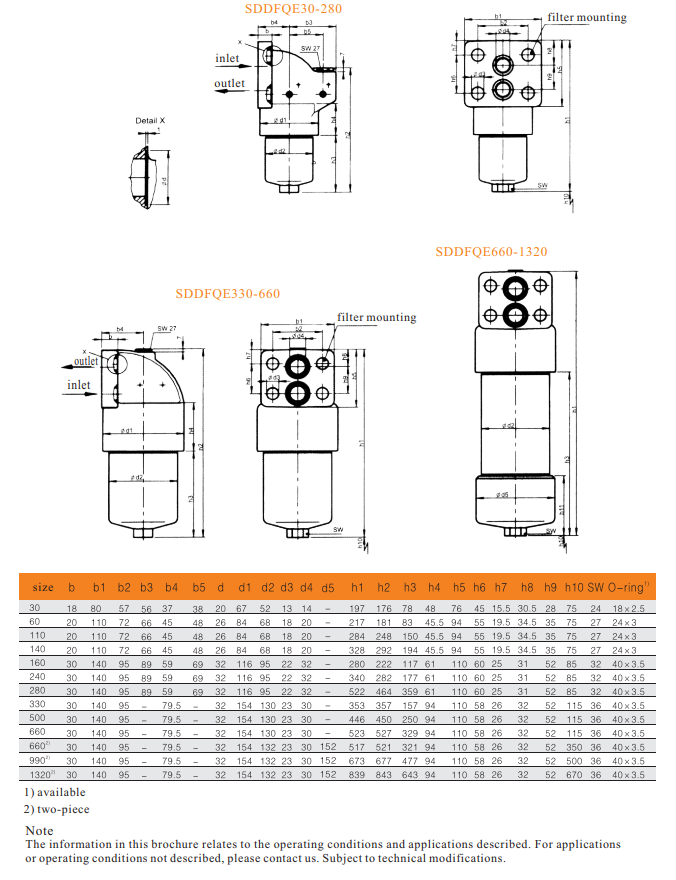
SDDF QE series pressure filters are designed in accordance with international regulation, which consist of a filter housing with a screw on cover plate.
Standard equipment
-mounting holes in the filter head
-two-piece bowl for size 660 and above
-compatibility with fire-resistant fluids HFA/HFC
-drain plug with pressure relief(size 330 and above)
Connection Diagram
Shengda is sure that our filters are of reliable performance so that they can protect hydraulic parts from polluting and machines from abrasion.
Filter elements are available with the following pressure stability values
BN/HC:25bar
BH/HC:210bar
W/HC:30bar
V:210bar
Seals
-NBR(=NBR)
Special models and accessories
-with bypass valve
-drain plug with pressure relief
-seals in FPM, EPDM
Grader Filter,High Pressure Filter,Flange-Mounted High Pressure Filter,Flange-Mounted Pressure Filter Xinxiang Shengda Filtration Technique Co., Ltd. , https://www.shengdafiltration.com