Many friends asked, what is the difference between a router and a Layer 3 switch? This is a good question, let's take a look at it today.
First, the working principle of the switch
When the switch receives the data, it checks its destination MAC address and then forwards the data out of the interface where the destination host is located. The reason why the switch can achieve this function is because the switch has a MAC address table inside, and the MAC address table records the corresponding information of all MAC addresses in the network and the ports of the switch. When a certain data frame needs to be forwarded, the switch searches the MAC address table according to the destination MAC address of the data frame, so as to obtain the port corresponding to the address, that is, the port on which the device having the MAC address is connected, and then the switch Forward data frames from this port.
1. The switch establishes a mapping between the address and the switch port according to the source MAC address in the received data frame, and writes it into the MAC address table.
2. The switch compares the destination MAC address in the data frame with the established MAC address table to determine which port to forward.
3. If the destination MAC address in the data frame is not in the MAC address table, it is forwarded to all ports. This process is called flooding.
4. Broadcast frames and multicast frames are forwarded to all ports.
Example: A network is shown in Figure 1.
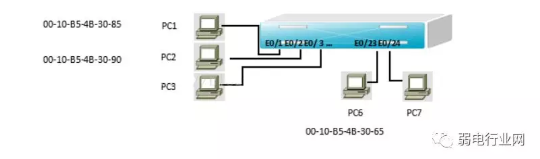
Figure 1 Switch Address Table

Table 1 Port/MAC Address Mapping Table
Assume that the host pc1 sends a data frame to the host pc7. After the data frame is sent to the switch, the switch first checks the MAC address table and finds that the host pc7 is connected to the E0/24 interface, and forwards the data frame from the E0/24 interface.
Three basic functions of the switch
1, learning
The Ethernet switch knows the MAC address of the device connected to each port, and maps the address to the corresponding port and stores it in the MAC address table in the switch cache.
2, forwarding / filtering
When the destination address of a data frame is mapped in the MAC address table, it is forwarded to the port connected to the destination node instead of all ports (if the data frame is a broadcast/multicast frame, it is forwarded to all ports)
3, eliminate the loop
When the switch includes a redundant loop, the Ethernet switch avoids loop generation through the spanning tree protocol, while allowing the existence of a backup path.
Comparison of second, second and third layer switches
1. Layer 2 switching technology
The Layer 2 switching technology is relatively mature. The Layer 2 switch is a data link layer device. It can identify the MAC address information in the data packet, forward it according to the MAC address, and record the MAC address and the corresponding port in its own internal. In the address table.
The specific workflow is as follows:
(1) When the switch receives a packet from a port, it first reads the source MAC address in the packet header so that it knows which port the source MAC address machine is connected to;
(2) Then read the destination MAC address in the packet header and look up the corresponding port in the address table;
(3) If there is a port corresponding to the destination MAC address in the table, copy the data packet directly to this port;
(4) If the corresponding port is not found in the table, the data packet is broadcast to all ports. When the destination machine responds to the source machine, the switch can learn which port the destination MAC address corresponds to, and the next time the data is transmitted. It is no longer necessary to broadcast all ports.
This process is continuously cycled, and the MAC address information of the entire network can be learned. The Layer 2 switch establishes and maintains its own address table.
From the working principle of the Layer 2 switch, the following three points can be inferred:
(1) Since the switch exchanges data of most ports at the same time, this requires a wide exchange bus bandwidth. If the Layer 2 switch has N ports, the bandwidth of each port is M, and the bandwidth of the switch bus exceeds N×M. Then the switch can achieve wire-speed switching;
(2) Learning the MAC address of the machine connected to the port, writing the address table, and the size of the address table (generally two representations: one is BEFFER RAM, one is the MAC entry value), and the address table size affects the access capacity of the switch. ;
(3) Another is that Layer 2 switches generally contain ASIC chips dedicated to packet forwarding, so the forwarding speed can be very fast. Because each manufacturer uses different ASICs, it directly affects product performance.
2, three-layer switch
The third layer exchange works in the third layer of the OSI seven-layer network model, that is, the network layer, which uses the header information of the IP packet in the third layer protocol to mark the subsequent data service flow, and the subsequent service flow with the same mark The message is switched to the Layer 2 data link layer to open a path between the source IP address and the destination IP address. This path passes through the second link layer. With this path, it is not necessary for the Layer 3 switch to unpack the received data packet every time to judge the route, but directly forward the data packet and exchange the data stream.
for example
For example, if A wants to send data to B and knows the destination IP, then A uses the subnet mask to obtain the network address and determines whether the destination IP is on the same network segment as itself.
Device using IP A------------ Layer 3 switch ---------------- Device B using IP
If it is on the same network segment but does not know the MAC address required to forward the data, A sends an ARP request, and B returns its MAC address. A uses this MAC to encapsulate the data packet and sends it to the switch. The switch uses the Layer 2 switching module to search. The MAC address table forwards the packet to the corresponding port.
If the destination IP address is not displayed on the same network segment, then A needs to communicate with B. If there is no corresponding MAC address entry in the flow cache entry, the first normal data packet is sent to a default gateway. This default gateway Generally, it is set in the operating system and corresponds to the Layer 3 routing module. Therefore, for data that is not the same subnet, the MAC address of the default gateway is first placed in the MAC table; then it is received by the Layer 3 routing module. This data packet, querying the routing table to determine the route to B, will construct a new frame header, where the MAC address of the default gateway is the source MAC address and the MAC address of the host B is the destination MAC address. Through a certain identification trigger mechanism, the correspondence between the MAC address and the forwarding port of the host A and the B is established, and the inflow cache entry table is recorded, and the data of the subsequent A to B is directly submitted to the layer 2 switching module. This is usually referred to as a route that is forwarded multiple times.
The characteristics of the three-layer exchange can be seen:
a. High-speed forwarding of data by hardware combination.
b. This is not a superposition of a simple Layer 2 switch and a router. The Layer 3 routing module is directly superimposed on the high-speed backplane bus of the Layer 2 switch, which breaks the interface rate limit of the traditional router and can reach a rate of several tens of Gbit/s. Counting backplane bandwidth, these are two important parameters of Layer 3 switch performance.
c. Simple routing software simplifies the routing process.
d. Most of the data forwarding, except for the necessary routing and routing software processing, are two-layer modules for high-speed forwarding. Most of the routing software is processed and efficiently optimized software, which is not simply copying the software in the router.
and so:
Layer 2 switch: based on MAC address
Layer 3 switch: with VLAN function, switching and routing, based on IP, is the network.
Third, the difference between routers and Layer 3 switches
The router is a three-layer device, but the three-layer switch can work on both the third and second layers.
In fact, there are still big differences between Layer 3 switches and routers:
1. The main functions are different. Although Layer 3 switches and routers have routing capabilities, they cannot be equated accordingly. The router not only has routing function, but also provides switch port and hardware firewall additional functions. The purpose is to make the device more applicable and more practical.
The same is true for Layer 3 switches. The main function is still data exchange, but it is a switch with some basic routing functions. The Layer 3 switch has both data switching and routing and forwarding functions, but its main function is data exchange. The router only has the main function of routing and forwarding.
2. The main applicable environment is different. The routing function of a Layer 3 switch is usually simpler because it faces a simple LAN connection. Features are far less complicated than routers. Its main purpose in LAN is to provide fast data exchange function, to meet the application characteristics of frequent LAN data exchange.
The router is different, although it is also suitable for the connection between LANs, but its routing function is more reflected in the interconnection between different types of networks, such as the connection between the LAN and the WAN, between the networks of different protocols. Connections, etc., have the advantage of selecting zui good routing, load sharing, link backup, and exchange of routing information with other networks. In addition, in order to connect with various types of networks, the interface type of the router is very rich, and the three-layer switch is generally only the same type of LAN interface, which is very simple.
3, the technology is not the same. Routers and Layer 3 switches have significant differences in packet switching operations.
Routers typically perform packet switching by a network processor-based or multi-core routing engine.
The Layer 3 switch performs packet switching through hardware. After the Layer 3 switch performs route lookup on the first packet sending control plane, it will generate a mapping table of MAC addresses and IP addresses for data plane lookup. When the same data stream passes again, it will be based on this table. Look up the table instead of sending the control plane again (that is, "one route, multiple exchanges").
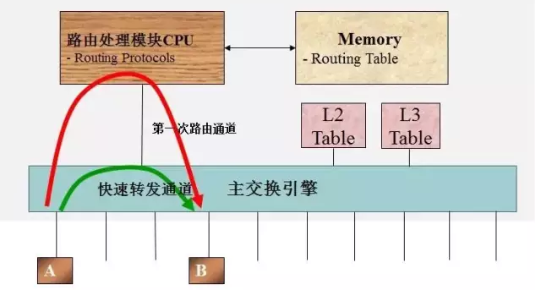
Improve the efficiency of packet forwarding. The route lookup of the Layer 3 switch is for data flow. It utilizes the cache technology and can be easily implemented by using ASIC technology. Therefore, it can greatly save costs and achieve fast forwarding.
The forwarding of the router adopts the longest matching method, which is complicated to implement. Generally, it is implemented by a high-cost network processor or a multi-core processor, and the number of routing tables is large and the cost is quite high.
Fourth, summary
Layer 2 switches are used in small local area networks. In small LANs, broadcast packets have little impact. The fast switching function of Layer 2 switches, multiple access ports and low price provide a perfect solution for small network users.
The most important function of the Layer 3 switch is to speed up the fast forwarding of data within the large LAN. The routing function is also used for this purpose. If the large-scale network is divided into small LANs according to departments, regions, etc., this will lead to a large number of Internet access, and the use of Layer 2 switches alone cannot achieve Internet access;
If the router is used simply, the number of interfaces is limited and the forwarding speed is slow, which will limit the speed and network scale of the network. It is an ideal choice for fast forwarding three-layer switches with routing function.
Uni-tanks
Beer Fermentation,Stainless Unitank,Conical Unitank,10Bbl Stainless Fermenter
WeBrew , https://www.thewebrew.com





